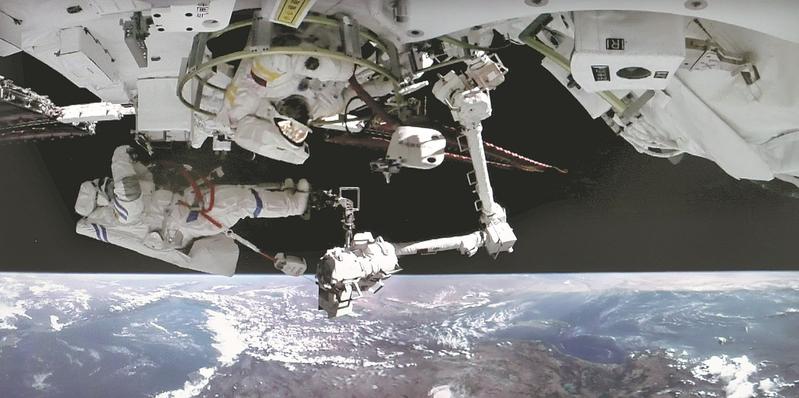
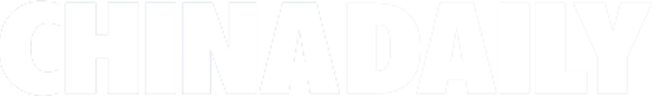 China's Shenzhou XIV astronauts Chen Dong (right) and Liu Yang exit the space station lab module Wentian on Sept 1, and use a robotic arm to install new instruments outside the Tiangong space station. This photo has been inverted top to bottom. (XU BU / FOR CHINA DAILY)
China's Shenzhou XIV astronauts Chen Dong (right) and Liu Yang exit the space station lab module Wentian on Sept 1, and use a robotic arm to install new instruments outside the Tiangong space station. This photo has been inverted top to bottom. (XU BU / FOR CHINA DAILY)
China's science and technology sector has seen profound changes over the past decade, characterized by more original breakthroughs in core technologies, higher academic output in both quantity and quality, and assuming a larger role in supporting the national economy, officials said.
The country's ranking in the Global Innovation Index rose from 34th in 2012 to 11th in 2022, according to the World Intellectual Property Organization.
Meanwhile, the National Bureau of Statistics said the nation's gross domestic research and development spending grew from 1.03 trillion yuan ($147.1 billion) in 2012 to more than 2.79 trillion yuan last year, when the R&D budget for basic research reached a record 181.7 billion yuan, 3.4 times higher than that in 2012.
According to the Ministry of Science and Technology, China also boasts the world's largest research workforce, with around 5.62 million full-time personnel last year, a rise of 1.7 times compared with 2012.
Speaking at a news briefing in June, Wang Zhigang, the minister of science and technology, said these scientific indicators show that China has become an innovative country. However, Wang noted that China still has many shortcomings in making original breakthroughs, training high-quality talent and obtaining key and core technologies.
As a result, the country will need to improve basic research, strengthen the role of private companies as pillars of innovation and create new engines for high-quality development through scientific and technological breakthroughs, he added.
As of this year, there are 173 national high-tech industrial development zones in China, 84 more than in 2012, according to the Ministry of Science and Technology.
Li Youping, deputy director of the ministry's Torch High Technology Industry Development Center, said that these zones are the vanguard of China's innovation-driven development strategy as they hold much of the nation's research resources and have contributed greatly to the national economy.
National high-tech zones are home to 84 percent of State Key Laboratories and 78 percent of national technological innovation centers, in addition to more than 4,400 research institutions.
The gross industrial output of these high-tech development zones grew from 5.4 trillion yuan in 2012 to 15.3 trillion yuan last year, and they contributed to 13.4 percent of China's GDP, while only using 2.5 percent of the land available for construction.
The number of high-tech companies in national high-tech zones also rose from less than 20,000 in 2012 to 115,000 last year, Li said.
With these resources, high-tech zones have made numerous breakthroughs in quantum technologies, high-speed rail, the Beidou Navigation Satellite System, the C919 passenger jet, 5G telecommunications and other fields of strategic significance, he added.
Meanwhile, China's first artificial intelligence chip, first quantum communication satellite, first vaccines for COVID-19 and many other breakthroughs were achieved by scientists and companies working in high-tech zones.
With regard to academic output, China overtook the United States as the world leader in both the quantity and quality of scientific papers published from 2018 to 2020, according to an annual report published last month by the National Institute of Science and Technology Policy in Japan.
Chinese research accounted for 27.2 percent, or 4,744 papers, of the world's top 1 percent of highly cited papers from 2018 to 2020. The US accounted for 24.9 percent, or 4,330 papers. It was the first time that China had surpassed the US in this prestigious category, the report noted.
These highly cited papers are studies that outperformed 99 percent of their peers based on the number of citations received. The number of citations is a commonly used measurement of a study's quality and influence.