The US deployment of the first Mid-Range Capability (MRC) missile system to the Philippines as part of an ongoing bilateral military exercise is a “black day” for the Asia-Pacific that threatens regional stability and further stirs tensions in the South China Sea, analysts said.
This is the first time that the United States has deployed a long-range weapon system to the Philippines. The Typhon missile system is being used as part of the joint Balikatan (shoulder-to-shoulder) military exercise taking place from April 22 to May 10.
The French navy is joining Balikatan for the first time, while officials from 14 countries — Brunei, Canada, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and Vietnam — will attend as observers
Anna Malindog-Uy, vice-president for external affairs at the Asian Century Philippines Strategic Studies Institute (ACPh), said the deployment of Typhon for this year’s Balikatan is a “black day” for the Asia-Pacific region that could reshape its security structure.
READ MORE: China opposes US deployment of ballistic missiles in Asia-Pacific
She said the deployment could potentially serve as a precursor to the more permanent basing of such missile systems in the Western Pacific region and “can be interpreted as provocative vis-a-vis China”.
Japanese media reported that the Typhon missile system has a range that reaches Shanghai from the Balikatan site.
Malindog-Uy said it might push China to take more assertive measures in the South China Sea while other member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) may view the deployment as the “beginning of a more volatile, unpredictable, and tension-driven regional security”. The Philippines is part of the 10-member regional bloc.
“The introduction of such capabilities on Philippine soil could contribute to a regional arms race, with other countries feeling pressured to develop or acquire similar or counterbalancing capabilities, potentially increasing the likelihood of an arms race in the region,” Malindog-Uy told China Daily.
The Balikatan is being conducted in the northern Philippine island of Luzon — which faces Taiwan of China — another flashpoint of tense China-US relations.
Oh Ei Sun, a senior fellow at the Singapore Institute of International Affairs, said owing to Sino-Philippine confrontation over the South China Sea and increased tensions between China and the US, it is “almost inevitable” that the US and the Philippines hold joint military exercises.
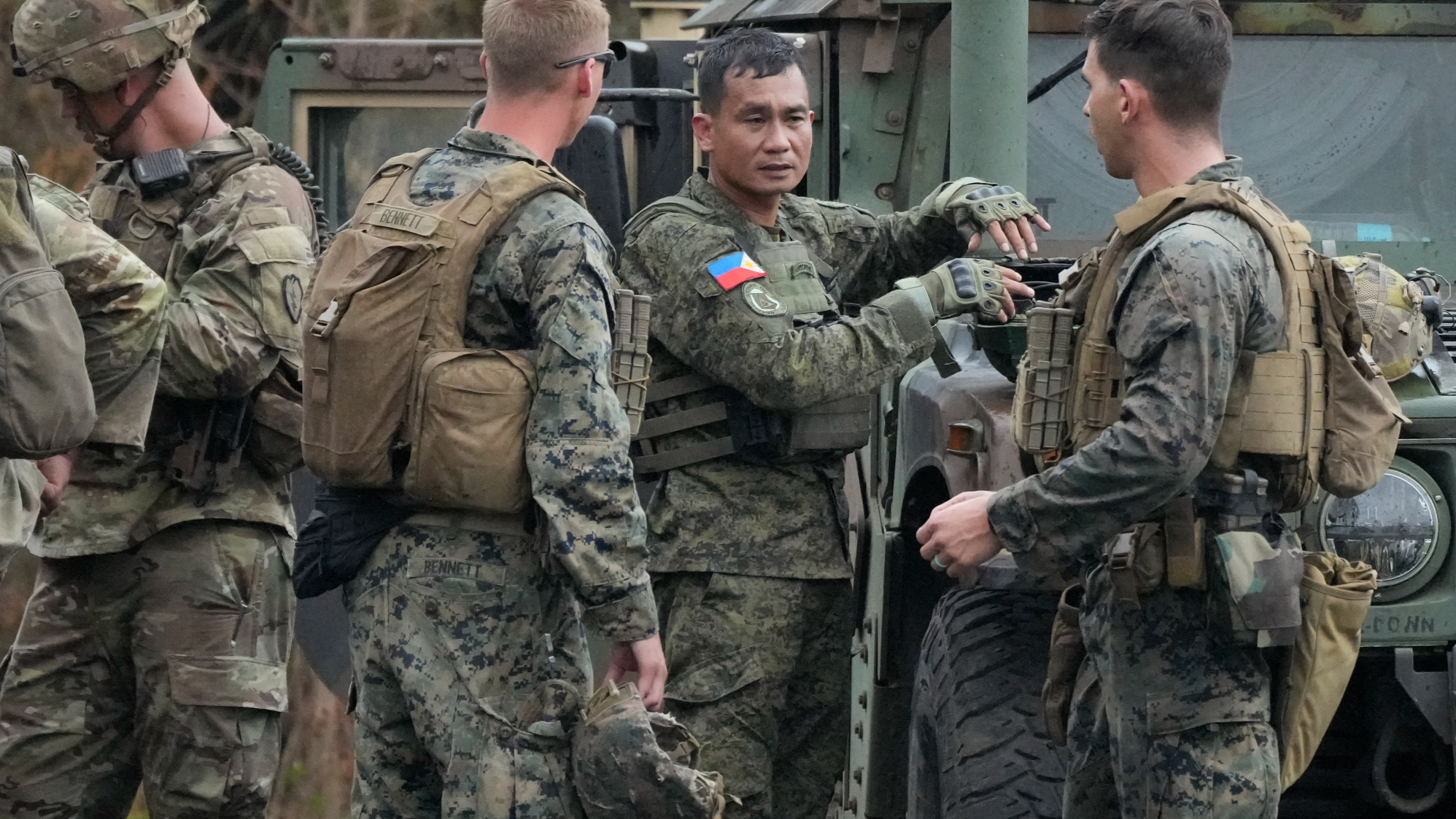

However, Philippine officials said in an April 20 press briefing that the country is not preparing for war.
Jonathan Malaya, assistant director general of the National Security Council, said “war is not on the table”. He said the US and the Philippines have been conducting Balikatan for the past few years, way before the tension over the South China Sea erupted, to improve Philippine defense capabilities.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Lin Jian said in an April 18 press briefing that the Philippines “should understand that drawing in countries outside the South China Sea to flex their muscles and stoke confrontation in the region will only intensify tensions and undermine regional stability”
According to Malaya, the Philippines will exhaust diplomatic means to settle the tension over the disputed waterway.
Over 16,000 soldiers are joining the 39th iteration of Balikatan. The French navy is joining Balikatan for the first time, while officials from 14 countries — Brunei, Canada, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and Vietnam — will attend as observers.
Wilson Lee Flores, honorary chairman of the Anvil Business Club, an association of Chinese-Filipino entrepreneurs, is hoping that the Balikatan can focus on transnational problems like sea piracy, marine pollution, and disaster relief instead of being “perceived as targeting other foreign countries”.
Flores said the Philippine constitution upholds an independent foreign policy and he expects that this year’s Balikatan will not “heighten tensions or cause any misunderstandings with other countries, for the sake of ASEAN stability and peace”.
He said ASEAN should aspire to become a nuclear-free and demilitarized region focused on economic growth, trade, investments, and tourism. “ASEAN should avoid tragic wars now plaguing Europe and the Middle East,” Flores said.

Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Lin Jian said in an April 18 press briefing that the Philippines “should understand that drawing in countries outside the South China Sea to flex their muscles and stoke confrontation in the region will only intensify tensions and undermine regional stability”.
READ MORE: Duterte voices concern over US military presence in Philippines
Lin said that by introducing external forces to maintain its security, the Philippines “will only put itself into greater insecurity and (it may) even become the pawn of others”.
Malindog-Uy of ACPh said the deployment of Typhon for this year’s Balikatan will contribute to shaping the security architecture in the Asia-Pacific region.
“The actual outcome will depend on the actions and reactions of the various stakeholders involved, their strategic calculations, and their engagement in diplomatic efforts to manage rising tensions and maintain peace and stability in the region,” she said.
Contact the writer at prime@chinadailyapac.com